Chapter IV Defense Expenditure and Defense Assets
China manages and uses its defense funds, ensures the procurement and supply of its military equipment and materials, and protects its defense assets in conformity with legal provisions and in accordance with the needs of national defense building and the requirements of the socialist market economy.
Pursuant to The National Defense Law, the Chinese government follows the guiding principle of the coordinated development of national defense and economy. Based on the economic development and revenue growth, it has continued to increase its defense expenditure moderately so as to keep up with the changes in the demands of national defense. China's GDP in 2002 and 2003 was 10,517.234 billion yuan and 11,725.194 billion yuan respectively. Its defense expenditure in 2002 and 2003 was 170.778 billion yuan and 190.787 billion yuan respectively. Its defense budget for 2004 is 211.701 billion yuan.
The increased part of China's defense expenditure has primarily been used for the following purposes: (1) Increase of the salaries and allowances of the military personnel. It is necessary to raise the salaries and allowances of the military personnel in step with the socio-economic development and the per-capita income rise of urban and rural residents. In the light of the unified wage adjustment policy for the personnel of state organs, China has raised the salary rates of officers, civil cadres and non-commissioned officers; the allowances of conscripts and cadets under the supply system; and the pensions of the retired. (2) Further improvement of the social insurance system for servicemen. In December 2003, the Provisional Measures on Social Insurance for Unemployed Accompanying Spouses of PLA Servicemen was formulated, to guarantee their basic living standard and provide them with social insurance subsidies. (3) Support for the structural and organizational reform of the military. China once again downsizes its military by 200,000, and has to increase the expenses on the resettlement of the discharged surplus personnel accordingly. (4) Increased investment in the development of high-caliber talents in the military. The PLA has established and refined an incentive mechanism for talented people, improved conditions in military educational institutions, and entrusted non-military colleges and universities with the education of qualified personnel, so as to ensure the achievement of the PLA's Strategic Project for Talented People. (5) Moderate increase of equipment expenses. This is aimed at promoting the leapfrog development of weaponry and equipment, and stepping up preparations for military struggle.
In the past two years, the percentages of China's annual defense expenditure to its GDP and to the state financial expenditure in the same period have remained basically stable. For most of the years since the 1990s, the growth rate of China's defense expenditure has been lower than that of the state financial expenditure.
The absolute amount of China's defense expenditure has long been lower than those of some major Western countries, and the proportion to the GDP and state financial expenditure has also been relatively low. In 2003, China's defense expenditure amounted to only 5.69% of that of the United States, 56.78% of that of Japan, 37.07% of that of the United Kingdom, and 75.94% of that of France.
The management of China's defense funds has become more transparent and standardized, and its cost-effectiveness has been steadily improving. The budgeting reform for defense expenditure has been further deepened, and a new defense budgeting system established, which introduces the zero-base budgeting method and united budgeting system. The budget adjustment and control function has been strengthened, and the input direction and amount of defense funds optimized. The tendering and bidding system for the procurement of defense materials, projects and services has been improved, and the scope of centralized payment extended.
Table 1: Percentage of China's Annual Defense Expenditure in Its GDP (1997-2003)
| Year | 1997 | 1998 | 1999 | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 |
| Percentage | 1.09 | 1.19 | 1.31 | 1.35 | 1.48 | 1.62 | 1.63 |
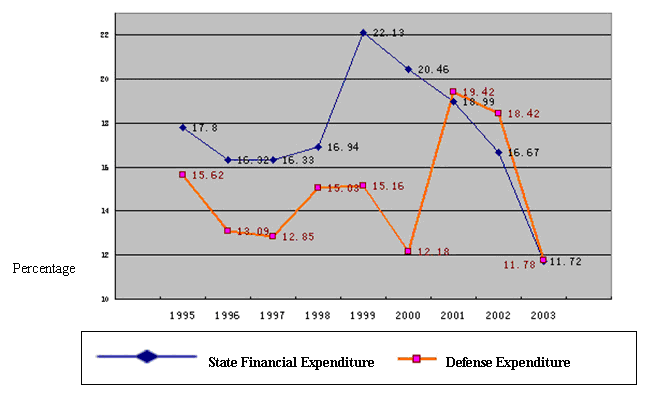 |
Chart 1: Comparison Between the Growth Rate of China's Defense Expenditure
and That of Its State Financial Expenditure (1995-2003)
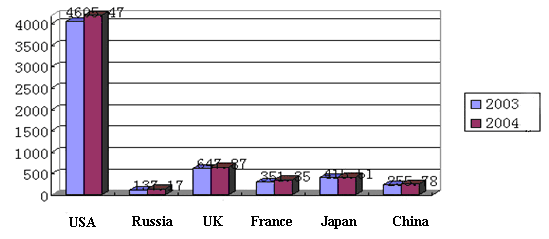 |
Chart 2: Comparison of the Defense Expenditures of Some Countries in 2003
and 2004 (unit: billion US dollars)
Note 1: Statistics in the charts are sourced from the national defense reports, financial reports and other government reports published by the said countries.
Note 2: The average exchange rate in 2003 was US$ 1.0 ˜ RMB 8.2770. On Nov. 20, 2004, US$ 1.0 ˜ RMB 8.2765.
Table 2: The Percentages of the Defense Expenditures in the GDP and Financial
Expenditures of Some Countries in 2003
| Country | USA | Russia | UK | France | Japan | China |
| Defense expend. as % of GD | 3.60 | 2.64 | 3.11 | 2.22 | 0.99 | 1.63 |
| Defense expend. as % of financial expenditure | 16.20 | 14.69 | 8.10 | 11.00 | 6.06 | 7.74 |
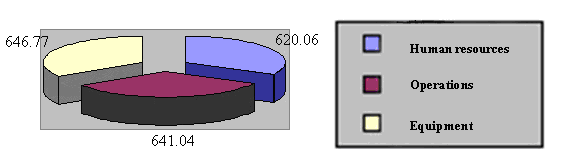 |
Chart 3: China's Defense Expenditure, 2003 by Proportion
(unit: RMB billion yuan)
Military Order Placement and Procurement
China practices a state ordering system to guarantee the procurement and provision of weapons, equipment and military materials. The General Armaments Department is responsible for the procurement of weaponry and equipment while the General Logistics Department is in charge of the procurement of military materials.
In October 2002, the CMC promulgated the Regulations on the Armaments Procurement of the PLA. In December 2003, the General Armaments Department issued relevant provisions, including the Provisions on the Management of Armaments Procurement Plans, the Provisions on the Management of Armaments Procurement Contracts, the Provisions on the Management of Armaments Procurement Modes and Procedures, the Provisions on the Management of the Examination of the Qualifications of Armaments Manufacturing Units and the Provisions on the Management of the Centralized Procurement of Armaments of the Same Kind. All these regulations and provisions constitute a new statutory system for the procurement of armaments. In recent years, the procurement of armaments has followed the basic principles of the government procurement system, gradually pulled down the sectional barriers in military industry, introduced the mechanism of competition and supported state-owned enterprises outside the military industry and private high-tech enterprises to enter the market of military products. The procurement mode has been in an accelerating transition from procurement at designated enterprises to multiple ways of procurement such as open bidding, invited bidding, competitive bargaining and inquiry procurement. This has raised the overall cost-effectiveness of armaments procurement and ensured the procurement at reasonable prices of weapons and equipment advanced in performance, superior in quality and complete as a set. The procurement of military computers and network devices, vehicle chassis, generating sets, shelters, and other types of general-purpose equipment has changed from separate to centralized procurement at the PLA level.
Since February 2002, in accordance with the Overall Plan for Deepening the Reform in the Procurement of Military Materials, Projects and Services approved for distribution by the CMC, the General Logistics Department has promulgated in succession the Provisions on the Management of the Procurement of Military Materials, the Provisions on the Management of Inviting Tenders for Military Materials, the Provisions on the Management of Procurement Contracts for Military Materials, the Provisions on the Management of the Price Review Work of Procurement Agencies of Military Materials, the Provisional Measures for the Management of Centralized Procurement Payment of Military Materials, Projects and Services, and the Provisions on Auditing the Procurement of Military Materials, Projects and Services. Following the basic principles of government procurement and taking into consideration the actual conditions of the building and management of the armed forces, the PLA has adopted in an all-round way a mode of procurement of military materials which focuses mainly on hierarchical management and centralized procurement. This mode has improved the operational mechanism of proper division of labor and mutual restraint among the departments in charge of funds, planning and procurement, and raised the level of standardization, specialization and informationalization in the procurement of materials as well as the cost-effectiveness resulting from large-scale procurement. Now procured in a centralized way are more than 1,000 kinds of materials in 24 categories needed in the development, training, scientific research and daily life of the armed forces. Procurement items included in the annual budget are procured through public bidding if their procurement value exceeds the quota. The quota prescribed by the General Logistics Department is RMB 500,000 yuan or more.
Defense assets are funds, land and other resources which the state has directly invested in or appropriated for the building of the armed forces, defense scientific research and production and other aspects of defense construction. They also include the resultant weaponry and equipment, installations and facilities, materials and technological achievements used for defense purposes. The defense assets possessed, used and managed by the PLA in accordance with the law belong to the PLA's state-owned assets. The state has promulgated the National Defense Law of the PRC, the Law of the PRC on Protecting Military Facilities, and the Implementation Measures for the Law of the PRC on Protecting Military Facilities. The PLA has formulated more than 30 rules and regulations on the management of its state-owned assets, such as the Provisions on the Management of the State-Owned Assets of the PLA. This has put the work of protecting defense assets on the legal track.
The people's governments and military organs at all levels jointly protect military facilities and safeguard national defense interests. Under the leadership of the State Council and the CMC, the General Staff Headquarters is in charge of the work of protecting military facilities throughout the country. The headquarters of the military area commands are in charge of the work of protecting military facilities within their areas of responsibility. In the areas where there are military facilities, the local governments at and above the county level and the relevant military organs stationed there jointly set up military facility protection committees, with their administrative offices established in the provincial commands (garrison commands), sub-commands (garrison commands) and the people's armed forces departments of counties, autonomous counties, cities and municipal districts. Following the guiding principle of providing categorized protection and ensuring the safety of key facilities, the state designates military forbidden zones and military restricted zones as a way to protect military facilities, and also takes appropriate measures to protect military facilities outside such zones. Protected by law are works for military operations, airspace clearance around military airports, military communication and power transmission lines, military oil and water pipelines, electromagnetic environments of fixed military radio installations, frontier defense installations and military survey marks.
Under the General Logistics Department is the Bureau of PLA's State-Owned
Assets Management in charge of the management of the PLA's state-owned
assets. The PLA's state-owned assets are managed under the system of unified
leadership and hierarchical responsibility. The logistics organ at each
level is responsible for management of the state-owned assets at its own
level. In recent years, the PLA has adopted a management method of property
inspection and registration and physical assets valuation and accounting,
and instituted a system of property right registration, assets assessment
and assets reporting, thus effectively standardizing the management of
the PLA's state-owned assets and ensuring their safety, integrity, appropriate
allocation and effective use.