| |
 China
lacks forests. Totaling 158.94 million hectares, forests cover 16.55 percent
of China's total land area, far less than the world's average level of
30.8 percent. Natural forests are concentrated in the northeast and the
southwest, but scarce in the densely inhabited and economically developed
eastern plains and the vast northwestern region. China
lacks forests. Totaling 158.94 million hectares, forests cover 16.55 percent
of China's total land area, far less than the world's average level of
30.8 percent. Natural forests are concentrated in the northeast and the
southwest, but scarce in the densely inhabited and economically developed
eastern plains and the vast northwestern region.
However, the forests in China are rich in tree species, with the number
of arbor species alone exceeding 2,800. Rare and peculiar species include
ginkgo and metasequoia (dawn redwood). In order to conserve environment
and meet the needs of economic construction, China has launched large-scale
afforestation campaigns. The area of planted forests has reached 33.79
million hectares, accounting for 31.86 percent of the nation's total forest
area, making China a country with the largest area of planted forests
in the world.
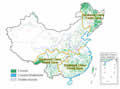
Northeast China Forest Zone Located in the Greater and Lesser
Hinggan Mountains and the Changbaishan Mountain, the Northeast China Forest
Zone is the largest natural forest area in China, with its forest coverage
and timber reserves accounting for over one-third of the national totals.
The area turns out half of the national total timber output. Chief tree
species include larch and Korean pine.
Southwest China Forest Zone China's second largest natural forest
area, the Southwest China Forest Zone consists of forests in the Hengduanshan
Mountains, on the southern slopes of the Himalayas and in the area at
the U-turn of the Yarlung Zangbo River. Its forest reserves make up one-third
of the national total. Main tree species include fir, red sandal and nanmu.
Southeast China Forest Zone Comprising mainly planted forests,
the Southeast China Forest Zone covers the vast hilly areas south of the
Qinling-Huaihe line and east of the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau. Economic tree
species are mainly planted in the zone, such as tea shrubs, moso bamboo,
masson pine and lacquer tree.
Shelter-forests In a bid to resist sandstorms and prevent soil
erosion, China has constructed many shelter-forests, such as the three-north
(northeast, north and northwest China) shelterbelt, shelter-forests along
the middle and upper reaches of the Yangtze River, coastal shelterbelt
networks, afforestation project in the Taihangshan Mountains and the plain
afforestation project. Of these, the three-north shelterbelt, extending
more than 7,000 km, has been regarded as "the world's greatest ecological
project." Covering 260 million hectares, it accounts for a quarter
of China's total land area.
|
|