  |
|
|
|
Governor: Han Changfu
Capital: Changchun
Government office address: 11 Xinfa Road, Changchun City
Tel: 0431-891 9971
Website: www.jl.gov.cn
|
|
|
|
|
|
Geographic location
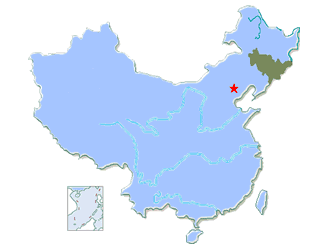
Jilin Province is located in the central part of northeast China, adjoining Heilongjiang in the north, Liaoning in the south, and Inner Mongolia in the west. It is adjacent to Russia in the east, and opposite to the North Korea in the southeast across the Tumen and Yalu rivers. Located between 122-131 degrees E and 41-46 degrees N, its territory covers 187,400 sq km, accounting for 2% of the nation's total. The land is high in the southeastern part and low in the northwestern, with a vast plain lying in its mid-west. |
|
|
|
|
|
General Economy
|
|
Gross domestic product (GDP)
|
GDP for 2005 was 361.492 billion yuan, up 12.0% from the previous year.
|
|
GDP ratio (primary, secondary and tertiary industries)
|
The primary industry yielded a value added of 60.7 billion yuan, 8.3% more than that of the previous year; the secondary industry, 160.513 billion yuan, a growth of 13.3%; the tertiary industry, 140.279 billion yuan, a growth of 12.3%. The GDP ratio of the three sectors is 16.8: 44.4: 38.8.
|
|
Revenue and expenditure
|
Provincial revenue was 41.86 billion yuan, an increase of 27.2% over the previous year. Provincial expenditure was 63.11 billion yuan, an increase of 24.3%.
|
|
Consumer price index (CPI)
|
CPI was 101.5, down 2.6 percentage points from the previous year.
|
|
Investment in fixed assets
|
Fixed asset investment was valued at 180.198 billion yuan, up by 53.8% from the previous year.
|
|
Major Industries
|
|
Agriculture
|
In 2005, the province's total grain production stood at 25.812 million tons, up 2.8% from 2004.
|
|
Industry
|
The industrial added value totaled 120.08 billion yuan, an increase of 11.0%.
|
|
Construction
|
Its output value totaled 48.522 billion yuan, up by 34.3%.
|
|
Transportation
|
Freight carried by various means of transport for the year was 2.3% up from the previous year to reach 375.286 million tons, which included 64.74 million tons by railway, up 1.4%; and 274.41 million tons by highway, up 2.9%.
The number of passengers carried by various means of transport was 2.0% up to reach 277.245 million persons, which included 46.181 million persons by railway, down 1.5%; 228.7 million persons by highway, up 2.6%; 1.13 million persons by waterway, up 4.6%; and 1.234 million persons by airway, up 18.4%.
|
|
Postal services
|
The annual turnover of postal operations totaled 1.33 billion yuan, up 17.7% from the previous year.
|
|
Telecommunications services
|
The annual turnover of telecommunications services totaled 24.83 billion yuan, up by 24.1%. At the end of 2005, the number of fixed line subscribers reached 7.686 million, up by 15.6% from 2004; and the number of mobile phone subscribers reached 9.157 million, up by 19.9%.
|
|
Retail
|
The annual turnover from retail sales reached 146.081 billion yuan, an increase of 11.8% from the previous year.
|
|
Tourism
|
Revenue from domestic tourism was 21.934 billion yuan, up 24.7% from the previous year, and foreign exchange earnings from tourism totaled US$120 million, up by 25.0%.
|
|
Continued Effects of Market Reform
|
|
Imports & exports
|
The annual value of imports and exports totaled US$6.528 billion, 3.9% down from the year before. Of this figure, US$2.467 billion was from exports, up 43.9%, while US$4.061 billion was from imports, down 20.0%.
|
|
Foreign investment
|
The foreign investment which was materialized during the year stood at US$1.151 billion, up by 100%.
|
|
Urban Construction and Management
|
|
Road transport
|
By the end of 2005, a total of 50,308 km of highways had opened to traffic, 6.5% up from the previous year-end. The rural highways linking villages totaled 37,092 km, up by 8.4% from 2004.
|
|
Social Undertakings
|
|
Science and technology
|
The number of technological contracts signed during the year reached 3,879, worth some 1.223 billion yuan, 13.3% up from the year before.
|
|
Education
|
The number of students enrolled in postgraduate schools and institutions of higher learning during the year stood at 13,200 and 129,400 respectively.
|
|
Culture
|
By the end of 2005, the province had a total of 61 arts performance organizations, 81 cultural and arts centers, 63 public libraries, and 18 museums. About 96.7% and 97.9% of the provincial population respectively had access to various radio and TV programs. The cable TV subscribers numbered 2.495 million at the year-end.
|
|
Public health
|
By the end of 2005, 53 of the 60 emergency medical service projects had been accomplished. 9 counties (cities) began to pilot the new rural cooperative medical service which had covered a total of 2.026 million of rural residents at the year-end, accounting for 63.5% of the total rural population.
|
|
Sports
|
During the year a new health and fitness center at the municipal level, and 13 at the county level were built. Indoor and outdoor body building facilities were also installed in 13 more urban communities and 21 more townships. By the year-end, the per capita share of public playgrounds stood at 1.47 square meters.
|
|
Welfare and aid
|
Various welfare units across the province were equipped with 45,200 beds and put up 36,000 homeless and vagrant people during the year. There were 3,000 urban community centers at the end of the year. The welfare lottery reaped sales of 960 million yuan in 2005. Public donations totaled 90 million yuan.
|
|
Population, Employment, Social Security and Living Standards
|
|
Population
|
The year 2005 saw births of 214,000, or a birth rate of 7.89‰, and deaths of 144,000, or a mortality rate of 5.32‰. The natural growth rate of the population stood at 2.57‰. At the end of the year, the total population stood at 27.16 million, an increase of 75,000 than the 2004 figure.
|
|
Employment
|
The employed population stood at 12.389 million, up by 1.4% from the previous year. A total of 571,400 new jobs were created during the year. About 349,000 laid-off workers got re-employed.
|
|
Registered unemployment rate
|
The number of registered unemployed population at the end of the year was 276,400, the registered urban unemployment rate being 4.2%.
|
|
Social security
|
In 2005, insurance plans for endowments, unemployment and medical treatment covered a population of 4.56 million, 1.99 million and 2.83 million respectively. The figures for endowments and medical treatment insurances are up by 3.9% and 4.8% respectively from the previous year. About 1.36 million urban residents received minimum living allowance from the government.
|
|
Residents' income
|
The disposable income of urban residents was 8,691 yuan per capita, up by 10.8% from 2004. Rural residents' per capita net income was 3,264 yuan, up 8.8%.
|
|
Geography and Natural Conditions
|
|
Elevation extremes
|
The eastern part of the province is the mountainous area of the Changbai Mountains with an elevation of over 1,000 meters and the Jidong hilly land of 500 meters above sea level or lower. The western part of the province is the Songliao Plain, whose low and level western section is the grain base of the province.
|
|
Climate
|
Jilin is located in the middle latitudes of the northern hemisphere, east of the Euro-Asian continent, the northernmost section of the temperate zone in China, nearing the sub-frigid zone. The eastern part of the province is close to the Yellow Sea and the Sea of Japan, where the atmosphere is moist often accompanied with much rain. The climate of its western part, which is far from the sea and approaches to the arid Mongolian Plateau, is dry. As a whole, the province has a distinct temperate continental monsoon climate with a clear-cut change of four seasons. The yearly average temperature of most part of the province is 3-5 °C. The annual time of sunshine is 2,200-3,000 hours. The annual average accumulated temperature in activity is 2,700-3,600°C. The precipitation of the province in a year is 550-910 mm and the frost-free period lasts 120-160 days. With hot and rainy days in the same season, it is good for farming. The frost period begins in the last 10 days of September and lasts until the end of April or early May.
|
|
Natural resources
|
The province is one of China's six major forestry areas. The Changbai Mountains stretching about 500 km is known as the "Changbai Sea of Forest." The province's land used for forestry covers 9.72 million hectares, accounting for 51.37% of the province's total and ranking the 12th in the country. Forests cover 7.98 million hectares, accounting for 82.04% of the total land used for forestry, ranking the eighth in the country. The province's storage of live limber is 840 million cubic meters, ranking the sixth in the country. The province's forest coverage is 42.4%. The highest summit of the province, the White Cloud Peak of the Changbai Mountains, is 2,691 meters above sea level.
The prairie in western Jilin is situated in the center of the Songjiang-Nenjiang Prairie, one of the famous grasslands in China. The prairie is known for its rich forage grasses for sheep, most of which are perennial rootstock and bushy grasses. It is also one of the breeding bases of commercial cattle and fine-wool sheep in northern China. There are 4.379 million hectares of grassland are available in the province, mainly in its western and eastern parts.
Its western part is the easternmost point of the Euro-Asian grassland, where the source of water is rich and the quality of grass is good. A part of the Horqin Grassland, it is Jilin's animal husbandry base.
The province is abundant in minerals with a total of 136 varieties of ores discovered. The number of surveyed mineral deposits is 93, 75 of which have been explored. The province's reserves of 22 minerals rank the top five in the country. Its main minerals include: coal with a reserve of nearly 2.1 billion tons; petroleum with a remaining potential reserve of 113.99 million tons; iron ores with a reserve of 460 million tons; gold with a reserve ranking the 13th in the nation; the reserves of 10 other minerals such as oil shale, diatomite and wollastonite rank the first in the country; veneer gabbro and carbon dioxide gas rank the second in the country; that of molybdenum and germanium rank the third; the remaining potential reserve of petroleum ranks the sixth in the country. Jilin is favored with nonmetallic mineral products and most of its export products are crude nonmetallic minerals and their products. The reserves of wollastonite, diatomite, bentonite, and refractory clay are rich enough for mining. The reserves of petroleum, natural gas and coal are also affluent.
There is a rich resource of wildlife in Jilin Province, particularly in the Changbai Mountains area. Jilin is the original producer of the worldwide famous Three Northeast China Treasures – ginseng, fur of marten and pilose antler. Its other products, such as glossy ganoderma, the tuber of elevated gastrodia, astragali, and pine mushroom, hedgehogt fungus, frog fat are all well-known at home and abroad.
There are about 2,300 species of plant in the Changbai Mountains, of which 900-odd are of high economic value. There are 870 varieties of medicinal herbs and more than 200 varieties of edible plants. Trees of quality timber for industrial use include Korean pine, Changbai pine, yeddo spruce, northeast China ash, yellow pineapple, Manchurian walnut catalpa, and linden. Chinese grapes, the fruit of Chinese magnoliavine, cowberry and haw are materials for brewing wine. There are 300 varieties of wild plants that provide a rich source for honey-making. Among its 437 species of wild animals, there are precious fur animals and feather fowls such as sables, otters, lynx, Manchurian tigers, leopards, and flowery-tail pheasants. Precious animals that can be used as medicinal materials include red deer, musk deer, brown bears, badgers, frogs, and wood frogs. Animals of high economic value include wild boars, roe deer, and grouses.
Agriculture and crops:
The province's soil is fertile, suitable for growing grains, beans, oil crops, beetroot, tobacco, jute, potato, ginseng, traditional Chinese medicinal herbs, and fruits. The province's sown area is 3.96 million hectares.
Its per capita consumption of grain, the commodity rate of grain, the volume of grains shipped to other provinces, and the export of corn are leading the country continuously for many years.
The province is China's largest base of commercial grain. It produces corn, soybean and rice.
The Song-Liao Plain in Jilin is an important grain base of the country and a world-known corn-growing zone.
|
|
Tourism resources
|
The province boasts rich tourism resources. In the provincial capital Changchun, there are the former government office of the Manchurian State established by the Japanese invaders during World War II, the Jingyuetan Forest Park, the Monument to the Martyrs of the Soviet Red Army, the Automobile Town, and the Changchun Film Studio. There are also the Jilin University, the Changchun Institute of Optical and Mechanical Engineering, and the Changchun University. Among its five-star hotels are Mingmen Hotel and the Shangri-la Hotel.
In Jilin City, there are the mountain city of Gaojuli on Mount Longtans; Beishan Park; the Songhua Lake in Fengman; the Baohai Ancient Tombs in Mount Liuding of Dunhua; the Chengzishan mountain city in Yanji; the Changbaishan Nature Reserve that covers a vast area in the three counties of Changbei, Antu and Fusong and boasts scenic spots such as the Heavenly Pond, waterfalls, and groups of hot springs and grand canyons.
In Tonghua, there is the Tomb of General Yang Jingyu. In Ji'an, there are the Wandu mountain city; Donggou Ancient Tombs; the General Mausoleum known as the "oriental pyramid" and the stone tablet of King Haotai. Furthermore, there is the Liao Pagoda in Nong'an and the group of volcanoes at Yitong.
|
|
|





