| Shuming
Duan, Xinsheng Zhao, Ruifu Wen, Jinjin Huang, Guanhua Pi,
Sxiang Zhang Shengli
Bi, Li Ruan, Xiaoping Dong* and SARS research team
Institute for Viral
Disease Control and Prevention, Chinese Center for Disease
control and Prevention, China
The
causal agent for SARS is considered as a novel coronavirus
that has never been described both in human and animals previously.
Using a SARS coronavirus strain CoV-P9, which was isolated
from pharyngeal swab of a probable diagnosed SARS patient
in Beijing, the stability in mimic human specimens, on the
surfaces of commonly used materials in household and in mimic
environment, as well as resistances to temperature and UV
irradiation were analyzed. The cytopathic effect (CPE) was
measured in cell line Vero-E6 30 h postinfection, with 106
TCID50 viruses at final concentration. The results
showed that SARS coronavirus in the testing condition could
survive in serum, 1:20 diluted sputum and feces for at least
96 h, whereas maintain in urine for at least 72 h with low
level of infectivity. Survival abilities on the surfaces of
eight different materials and in water were quite comparable,
revealing reduction of infectivity 72 to 96 h exposure. Viruses
stayed stably at 4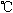 ,
room temperature (20 ,
room temperature (20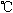 )
and 37 )
and 37 for at least 5 days without any change in the infectious ability
in cells, but converted to be non-infectious after 90-, 60-
and 30-min exposure at 56
for at least 5 days without any change in the infectious ability
in cells, but converted to be non-infectious after 90-, 60-
and 30-min exposure at 56 ,
67 ,
67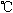 and
75 and
75 .
Irradiation of UV for 60 min on the virus in culture medium
resulted in destroying viral infectivity to undetectable level.
Collecting the results, the survival ability of SARS coronavirus
in human specimens and in environments seems to be relative
string. Heating and UV irradiation can eliminate the viral
infectivity efficiently. .
Irradiation of UV for 60 min on the virus in culture medium
resulted in destroying viral infectivity to undetectable level.
Collecting the results, the survival ability of SARS coronavirus
in human specimens and in environments seems to be relative
string. Heating and UV irradiation can eliminate the viral
infectivity efficiently.
|

