| |
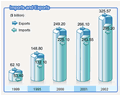
Rapid growth was registered in foreign trade. Total
value of imports and exports in 2002 reached $620.8 billion, up
21.8 percent over the previous year. The value of exports was
$325.6 billion, up 22.3 percent, and that of imports was $295.2
billion, up 21.2 percent.
 Growth
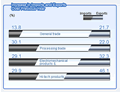
at varying degrees was seen in exports to major trade partners.
In 2002, China's export to the United States was $70 billion,
up 28.9 percent over the previous year; to Hong Kong SAR $58.5
billion, up 25.6 percent; to Japan $48.4 billion, up 7.8 percent;
to EU countries $48.2 billion, up 17.9 percent; to ASEAN members
$23.6 billion, up 28.3 percent; to the Republic of Korea $15.5
billion, up 23.8 percent; to Taiwan Province $6.6 billion, up
31.7 percent; and to Russia $3.5 billion, up 29.9 percent. Growth
at varying degrees was seen in exports to major trade partners.
In 2002, China's export to the United States was $70 billion,
up 28.9 percent over the previous year; to Hong Kong SAR $58.5
billion, up 25.6 percent; to Japan $48.4 billion, up 7.8 percent;
to EU countries $48.2 billion, up 17.9 percent; to ASEAN members
$23.6 billion, up 28.3 percent; to the Republic of Korea $15.5
billion, up 23.8 percent; to Taiwan Province $6.6 billion, up
31.7 percent; and to Russia $3.5 billion, up 29.9 percent.
 Foreign
direct investment increased steadily. In 2002, the contracted
foreign capital through foreign direct investment stood at $82.8
billion, up 19.6 percent, and the foreign capital actually utilized
was $52.7 billion, up 12.5 percent. By the end of 2002, China
had approved 424,196 foreign-funded enterprises, with foreign
contracted investment reaching $828.06 billion and foreign capital
actually utilized totaling $447.97 billion. Foreign
direct investment increased steadily. In 2002, the contracted
foreign capital through foreign direct investment stood at $82.8
billion, up 19.6 percent, and the foreign capital actually utilized
was $52.7 billion, up 12.5 percent. By the end of 2002, China
had approved 424,196 foreign-funded enterprises, with foreign
contracted investment reaching $828.06 billion and foreign capital
actually utilized totaling $447.97 billion.
Foreign economic and technical cooperation maintained good momentum.
In 2002, the accomplished business revenue through contracted
projects and labor contracts was $14.4 billion, up 18.2 percent.
The value involved in the new contracts signed was $17.9 billion,
up 8.7 percent.
Customs tariffs were reduced but revenue increased
in 2002. Revenue from tariffs has always been an importance source
of China's central finance, accounting for about one-third of
the central finance. The year 2002 was the first year after China's
WTO entry and to fulfill its commitments for tariff concessions
pledged for the year 2002, the Chinese Government adjusted tariff
rates beginning from January 1. The rates for 5,332 taxable items
of commodities were reduced at varying degrees and as a result,
China's general tariff level dropped from 15.3 percent to 12 percent.
However, thanks to the favorable situation in foreign trade, the
state treasury took in a total of 259 billion yuan in tariffs
and import-related duties, a new high.
 Strenuous
efforts were made to crack down on smuggling. From 1998 to 2002,
customs offices throughout the country seized 55,755 smuggling
cases with smuggled goods valued at 43.04 billion yuan. Large-scale
smuggling, which had once been rampant in the country, was brought
under effective control. After a customs anti-smuggling task force
was initiated in 1999, 14,955 suspected smugglers were held for
coercive measures and 7,791 of them were transferred to procuratorial
organs. Strenuous
efforts were made to crack down on smuggling. From 1998 to 2002,
customs offices throughout the country seized 55,755 smuggling
cases with smuggled goods valued at 43.04 billion yuan. Large-scale
smuggling, which had once been rampant in the country, was brought
under effective control. After a customs anti-smuggling task force
was initiated in 1999, 14,955 suspected smugglers were held for
coercive measures and 7,791 of them were transferred to procuratorial
organs.
Some goods will continue management by export licensing
in 2003. To safeguard normal export order and guarantee the sound
development of exports, China will continue to manage 52 categories
of bulk and sensitive goods by means of export licensing in 2003,
including export quota license, export quota tender, paid use
of export quota, free tender for export quota and export permit.
Goods under the management of export licensing included live cattle,
live pigs and live chicken targeting markets other than Hong Kong
and Macao, and beef, pork, chicken, garlic, heavy water, ozone-consuming
materials, controlled chemicals, platinum (exported in the form
of processing trade) and computers.
|