| |
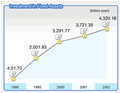
Investment in fixed assets kept growing fast in 2002. The completed
investment in fixed assets nationwide in 2002 was 4.32 trillion
yuan, exceeding 4 trillion yuan for the first time, up 16.1 percent
over the previous year, representing the highest growth rate since
1996.
 Overall
growth was seen in investment in eastern, central and western
areas in China. Of the total investment of state-owned units and
units with other types of ownership, the investment in eastern
areas was 1.85 trillion yuan, up 16.2 percent over the previous
year, or 2.9 percentage points higher; that in central areas was
758 billion yuan, up 20 percent, or 3.7 percentage points higher;
and that in western areas was 567.2 billion yuan, up 20.6 percent,
or 1.3 percentage points higher. Overall
growth was seen in investment in eastern, central and western
areas in China. Of the total investment of state-owned units and
units with other types of ownership, the investment in eastern
areas was 1.85 trillion yuan, up 16.2 percent over the previous
year, or 2.9 percentage points higher; that in central areas was
758 billion yuan, up 20 percent, or 3.7 percentage points higher;
and that in western areas was 567.2 billion yuan, up 20.6 percent,
or 1.3 percentage points higher.
Investment structure was further improved. In 2002, the investment
in the primary industry was 110.6 billion yuan, up 23.5 percent
over the previous year, representing the feature of recovery.
Investment in the secondary industry was 1.07 trillion yuan, up
22.9 percent, showing the trend of accelerated growth. Investment
in the tertiary industry kept fast growth, with a total completed
investment of 2.11 trillion yuan for the whole year, up 14.4 percent.
 The
construction of key projects progressed smoothly, including the
successful damming of the headrace and the completion of the principal
part of the main dam on the left side of the Three Gorges Project;
the smooth progress of the construction of Qinghai-Tibet Railway;
the quickened pace in the construction of west-to-east electricity
transmission project; and the start of the west-to-east natural
gas transmission project and the south-to-north water diversion
project. New headway was made in technical updating and transformation
of enterprises, which played an important role in the restructuring
endeavor. The
construction of key projects progressed smoothly, including the
successful damming of the headrace and the completion of the principal
part of the main dam on the left side of the Three Gorges Project;
the smooth progress of the construction of Qinghai-Tibet Railway;
the quickened pace in the construction of west-to-east electricity
transmission project; and the start of the west-to-east natural
gas transmission project and the south-to-north water diversion
project. New headway was made in technical updating and transformation
of enterprises, which played an important role in the restructuring
endeavor.
All the four major projects in the 10th Five-Year Plan (2001-05)
have begun construction. In March 2001, the Fourth Session of
the Ninth National People's Congress passed the Outline of the
10th Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development.
According to the outline, four projects-the Qinghai-Tibet Railway,
the west-to-east electricity transmission, the west-to-east natural
gas transmission and the south-to-north water diversion-would
start construction successively within five years. By December
27, 2002, when the south-to-north water diversion project was
officially launched, all the four major projects had started construction.
The Qinghai-Tibet Railway is the longest and highest plateau
railway in the world. Its construction started on June 29, 2001,
and a total investment of 5.3 billion yuan was completed in 2002,
with 121 km of rails laid down. The Kunlunshan Tunnel and Fenghuoshan
Tunnel were put through, and the construction team advanced to
the section between the Kunlunshan Mountains and the Tanggulashan
Mountains, 4,500-5,000 meters above sea level.
The west-to-east electricity transmission project has three routes-the
southern one, the central one and the northern one. Its construction
started in July 2001. Currently, construction of the three passages
is in full swing.
The west-to-east natural gas transmission project started construction
in July 2002. The pipeline extends 4,000 km eastward from Lunnan
County of the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region to Shanghai Municipality,
crossing 10 provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities.
It is designed to transmit 12 billion cubic meters of natural
gas annually. Investment in pipeline laying is expected to exceed
40 billion yuan and the total investment is expected to top 140
billion yuan. Construction has begun on 1,828 km of the pipeline.
The first phase on the eastern line and the first phase on the
central line of the south-to-north water diversion project, which
started construction at the end of 2002, involve a total static
investment of more than 150 billion yuan. On completion, the project
will increase the water supply in the northern regions by 13.4
billion cubic meters. While its top priority is to alleviate severe
water shortages in north China, the diversion project will also
rationally allocate the water resources of four major river valleys,
namely, the Yangtze River, the Yellow River, the Huaihe River
and the Haihe River.
Completion of the four major projects is expected to realize
large-scale resources readjustments nationwide, which would change
the layout of the Chinese economy.
|