| |
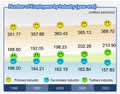
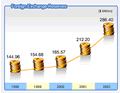
 In
2002, the gross domestic product (GDP) of China reached 10.24 trillion
yuan, up 8 percent over the previous year at comparable prices.
The added value of the primary industry was 1.49 trillion yuan,
up 2.9 percent. The added value of the secondary industry was 5.3
trillion yuan, up 9.9 percent. The added value of the tertiary industry
was 3.45 trillion yuan, up 7.3 percent. In
2002, the gross domestic product (GDP) of China reached 10.24 trillion
yuan, up 8 percent over the previous year at comparable prices.
The added value of the primary industry was 1.49 trillion yuan,
up 2.9 percent. The added value of the secondary industry was 5.3
trillion yuan, up 9.9 percent. The added value of the tertiary industry
was 3.45 trillion yuan, up 7.3 percent.
The general level of consumer prices in China in 2002 was down
0.8 percent  from
the previous year. Of this total, the consumer price level in
urban areas dropped by 1 percent and in rural areas by 0.4 percent.
The retail prices for commodities dropped by 1.3 percent, the
producers' prices for manufactured goods dropped by 2.2 percent,
and the purchasing prices for raw materials, fuels and power went
down by 2.3 percent. The prices for investment in fixed assets
were up 0.2 percent. Prices of service items in household consumption
rose 1.8 percent. from
the previous year. Of this total, the consumer price level in
urban areas dropped by 1 percent and in rural areas by 0.4 percent.
The retail prices for commodities dropped by 1.3 percent, the
producers' prices for manufactured goods dropped by 2.2 percent,
and the purchasing prices for raw materials, fuels and power went
down by 2.3 percent. The prices for investment in fixed assets
were up 0.2 percent. Prices of service items in household consumption
rose 1.8 percent.
 By
the end of 2002, the number of employed people in China totaled
737.4 million, or 7.15 million more than that at the end of 2001.
Of this total, 247.8 million were in urban areas, an increase
of 8.4 million over that at the end of 2001. At the end of 2002,
the number of workers laid off from state-owned enterprises and
not re-employed was 4.1 million, or 1.05 million less than the
previous year. The urban unemployment rate through unemployment
registration was 4 percent at the end of 2002, up 0.4 percentage
points. According to statistics of the Ministry of Agriculture,
by the end of 2002, the number of people employed in rural enterprises
totaled 133 million. That means a quarter of China's rural labor
had moved out of farming, transferring from agriculture to non-agricultural
sectors. By
the end of 2002, the number of employed people in China totaled
737.4 million, or 7.15 million more than that at the end of 2001.
Of this total, 247.8 million were in urban areas, an increase
of 8.4 million over that at the end of 2001. At the end of 2002,
the number of workers laid off from state-owned enterprises and
not re-employed was 4.1 million, or 1.05 million less than the
previous year. The urban unemployment rate through unemployment
registration was 4 percent at the end of 2002, up 0.4 percentage
points. According to statistics of the Ministry of Agriculture,
by the end of 2002, the number of people employed in rural enterprises
totaled 133 million. That means a quarter of China's rural labor
had moved out of farming, transferring from agriculture to non-agricultural
sectors.
 In
2002, China's trade surplus was $30.4 billion. The actually utilized
foreign direct investment during the year was $52.7 billion, up
12.5 percent over 2001. By the end of 2002, China's foreign exchange
reserves had reached $286.4 billion, an increase of $74.2 billion
over the pervious year. The exchange rate of the RMB was stable,
standing at $1 to 8.2773 yuan at the end of the year. In
2002, China's trade surplus was $30.4 billion. The actually utilized
foreign direct investment during the year was $52.7 billion, up
12.5 percent over 2001. By the end of 2002, China's foreign exchange
reserves had reached $286.4 billion, an increase of $74.2 billion
over the pervious year. The exchange rate of the RMB was stable,
standing at $1 to 8.2773 yuan at the end of the year.
 The
year 2002 saw market competition take initial shape after deepened
reforms in monopoly-controlled sectors such as telecommunications,
civil aviation, and power generation and supply. The reform and
loss reduction of enterprises in the defense industry progressed
smoothly. Reforms continued in the fields of government finance
and taxation, banking, social security, and circulation systems
for grain and cotton. Reform of the administrative procedures
for examination and approval sped up. Experiments in the reform
of the tax and fee collection system in rural areas were gradually
expanded and notable progress was made. Positive advancement was
scored in the development of the western region, with accelerated
progress in the construction of infrastructure and conservation
of ecological environment. Agricultural The
year 2002 saw market competition take initial shape after deepened
reforms in monopoly-controlled sectors such as telecommunications,
civil aviation, and power generation and supply. The reform and
loss reduction of enterprises in the defense industry progressed
smoothly. Reforms continued in the fields of government finance
and taxation, banking, social security, and circulation systems
for grain and cotton. Reform of the administrative procedures
for examination and approval sped up. Experiments in the reform
of the tax and fee collection system in rural areas were gradually
expanded and notable progress was made. Positive advancement was
scored in the development of the western region, with accelerated
progress in the construction of infrastructure and conservation
of ecological environment. Agricultural 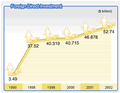 production
quickened its pace toward regional concentration, quality improvement
and industrialization. Adjustment of industrial structure was
accelerated by expanding the share of industries with high or
new technologies represented by information technology. Innovation
took place in domestic trade, reflected by the rapid development
of modern circulation and distribution systems. production
quickened its pace toward regional concentration, quality improvement
and industrialization. Adjustment of industrial structure was
accelerated by expanding the share of industries with high or
new technologies represented by information technology. Innovation
took place in domestic trade, reflected by the rapid development
of modern circulation and distribution systems.
 Main
problems that remained in economic performance included: the constraints
of insufficient effective demand and irrational supply structure
on economic growth, still high pressure for employment, problems
in increasing farmers' incomes, difficulties in the lives of some
urban and rural households, persistent market disorder, and occasional
occurrence of serious production accidents. Statistics showed
that in 2002, there were altogether 1.07 million accidents of
various types throughout the country, which caused 139,400 deaths.
Of those, 128 accidents incurred more than 10 deaths at one time,
totaling 2,341 deaths. Main
problems that remained in economic performance included: the constraints
of insufficient effective demand and irrational supply structure
on economic growth, still high pressure for employment, problems
in increasing farmers' incomes, difficulties in the lives of some
urban and rural households, persistent market disorder, and occasional
occurrence of serious production accidents. Statistics showed
that in 2002, there were altogether 1.07 million accidents of
various types throughout the country, which caused 139,400 deaths.
Of those, 128 accidents incurred more than 10 deaths at one time,
totaling 2,341 deaths.
|